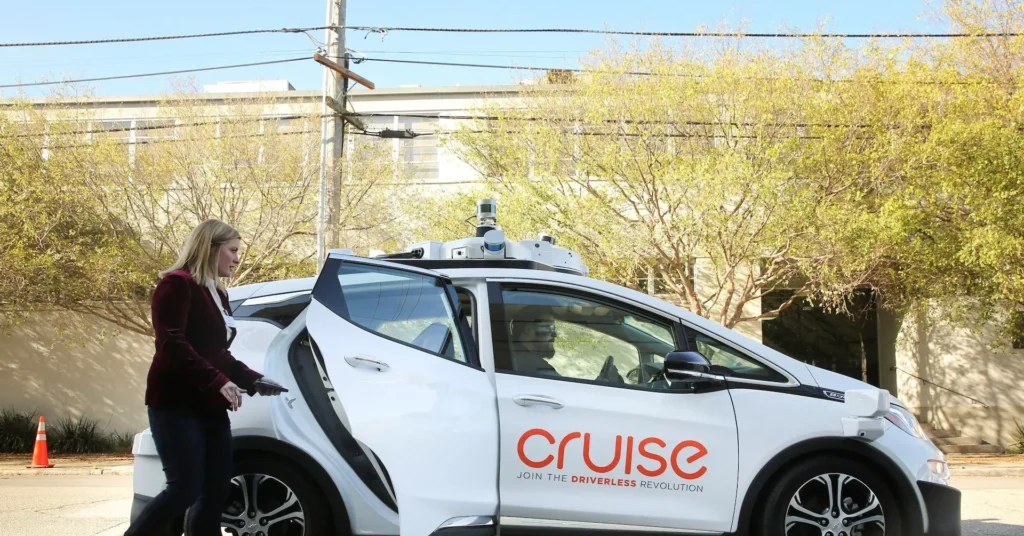
Have you ever imagined a world where cars drive themselves? Well, some companies like Waymo and Tesla are making it happen with their robotaxis! But not everyone is on board with this idea. General Motors, one of the biggest car makers in America, has decided to cut back on its robotaxi business called Cruise. They’re laying off many workers and even saying goodbye to some top leaders. In this article, we will explore why GM is shifting gears from robotaxis to focusing on making cars that can drive themselves safely for their owners. Let’s dive into this exciting story!
| Category | Details |
|---|---|
| Company Name | General Motors (GM) |
| Business Unit | Cruise (Robotaxi Service) |
| Recent Changes | Laying off nearly half of Cruise’s workforce (about 1,000 employees) |
| Key Departures | CEO Marc Whitten and other executives leaving the company |
| Reason for Layoffs | Shift in focus from robotaxi services to personal vehicle technology (Super Cruise) |
| GM’s Investment in Cruise | $10 billion |
| Projected Revenue from Autonomous Features | Up to $2 billion annually within five years |
| Cruise’s Safety Issues | Involved in serious accidents and required human intervention frequently |
| Impact on San Francisco Residents | Less autonomous vehicles on the streets, improving safety |
GM’s Big Changes in the Robotaxi World
General Motors (GM) is making significant changes in its approach to autonomous vehicles, particularly with its Cruise division. Recently, GM announced that it would be laying off nearly half of the Cruise workforce, which means about 1,000 employees will be losing their jobs. This decision comes after GM decided to fully acquire Cruise, indicating a shift in strategy. The company is now focusing on developing autonomous technology for personal vehicles instead of continuing with the robotaxi service.
This change has sparked discussions about the future of robotaxi services, especially as competitors like Waymo and Tesla are expanding their operations. By moving away from the robotaxi business, GM aims to invest more in features like their Super Cruise technology. This could potentially be more profitable for the company, leading to new opportunities in the personal vehicle market while allowing them to reallocate resources away from a service that has faced several challenges.
Why GM is Shifting Focus from Robotaxis
The decision to step back from the robotaxi initiative is primarily driven by financial concerns. GM has poured around $10 billion into Cruise, but the robotaxi service has not delivered the expected results. With incidents involving serious injuries and accidents, such as a pedestrian being struck by a Cruise vehicle, GM is reevaluating the safety and effectiveness of their autonomous technology. The company believes that focusing on personal vehicle features could help generate more revenue.
Additionally, GM’s management sees a promising future in charging consumers for access to autonomous features in cars. They project that these features could bring in up to $2 billion annually within five years. By prioritizing technology like Super Cruise, GM is looking to create a safer and more profitable business model, which may ultimately benefit their customers by improving the driving experience without the risks associated with robotaxis.
The Impact of Cruise’s Changes on San Francisco
The changes at GM’s Cruise division are likely to have a significant impact on the streets of San Francisco. The city’s residents have faced challenges with Cruise’s robotaxis, including incidents that caused traffic jams and even accidents. For example, there was an incident where multiple Cruise vehicles blocked traffic for hours. With GM’s decision to exit the robotaxi business, residents can expect less disruption and a safer environment on their streets.
Moreover, this shift could lead to an improved focus on safety and technology in personal vehicles. As Cruise moves away from robotaxis, the emphasis on developing reliable systems for everyday cars may enhance the driving experience. This change could also reduce public anxiety about autonomous vehicles roaming the streets, allowing San Francisco residents to feel more at ease without the presence of self-driving cars that have proven to be problematic.
The Implications of GM’s Exit from the Robotaxi Market
GM’s withdrawal from the robotaxi business highlights significant implications for the future of autonomous vehicle technology. As the largest automaker in the U.S. pulls back, it raises questions about the viability of robotaxi services in urban environments. This shift might deter other companies from investing heavily in similar projects, fearing that the financial risks outweigh potential rewards. With GM focusing on personal vehicle technology, the competitive landscape for robotaxis could drastically change, leading to a slower rollout of these services.
Moreover, GM’s exit signifies a pivotal moment for stakeholders in the autonomous vehicle sector. Investors may reassess their commitments to companies pursuing robotaxi services, especially those that have yet to prove their profitability. This could lead to a consolidation of resources within the industry, as firms that rely on robotaxi models may struggle to sustain operations without the backing of major players like GM. Ultimately, this could push innovation towards safer and more reliable autonomous technologies for personal use.
Understanding GM’s Shift to Super Cruise Technology
GM’s redirection towards its Super Cruise technology underscores a strategic pivot aimed at leveraging existing consumer markets. By enhancing its Super Cruise system, GM aims to monetize autonomous features through subscription models, projecting significant revenue growth in upcoming years. This approach not only capitalizes on an already established customer base but also aligns with consumer preferences for safer and more convenient driving experiences. With a focus on personal vehicle automation, GM is betting on a more immediate return on investment compared to the robotaxi model.
Additionally, Super Cruise presents a safer alternative to the robotaxi venture, which has faced scrutiny due to safety incidents. By prioritizing the integration of autonomous technology into personal cars, GM can maintain tighter control over user experiences and safety outcomes. This strategy not only helps avoid public relations disasters associated with robotaxi failures but also allows for gradual technology adoption among consumers, fostering trust in autonomous driving capabilities. GM’s move could redefine how consumers engage with self-driving features in their everyday lives.
The Future of Autonomous Vehicles Post-GM’s Decision
In light of GM’s recent decisions, the future of autonomous vehicles may see a shift towards more conservative development strategies. Companies like Waymo and Tesla, which continue to push ahead with robotaxi services, will now face increased scrutiny and pressure to demonstrate the safety and reliability of their technologies. The challenges GM encountered could serve as a cautionary tale for these firms, emphasizing the need for thorough testing and public reassurance before broad deployment of self-driving services.
Furthermore, GM’s pivot could inspire other automakers to reconsider their strategies regarding autonomous technology. As the industry evolves, there’s potential for a renewed focus on hybrid models that integrate autonomous features in personal vehicles rather than relying solely on robotaxi services. This could encourage a more widespread acceptance of autonomous driving, as consumers may prefer to experience these technologies in a familiar context, enhancing the overall safety and acceptance of such innovations in their daily lives.
Impact on Employment and Workforce in the Autonomous Sector
The significant layoffs at Cruise reflect broader trends affecting the autonomous vehicle workforce as companies navigate the financial realities of their investments. With GM cutting nearly half of its workforce at Cruise, employees face uncertainty in an industry that was once considered the future of transportation. This shift may lead to a talent drain as skilled workers seek opportunities in more stable sectors or companies that are still committed to the robotaxi model. The impact on employment raises concerns about the sustainability of the autonomous vehicle workforce.
On the other hand, these layoffs may also spur innovation in the job market as displaced workers apply their skills in other areas of the automotive and technology industries. As GM focuses on personal vehicle technologies, there may be emerging opportunities in software development, safety technology, and consumer vehicle automation. The challenge will be to adapt and reskill the workforce to meet the evolving demands of the industry, ensuring that the talent pool remains robust as autonomous technologies continue to develop.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a robotaxi and how does it work?
A **robotaxi** is a self-driving car that can pick you up and take you places without a human driver. It uses special **sensors** and **computers** to navigate the roads safely.
Why did GM decide to cut back on its robotaxi program?
GM cut back on its robotaxi program because it was losing a lot of money and faced serious **safety issues**. They want to focus more on making self-driving features for personal cars instead.
What happened to the employees at Cruise after the layoffs?
Around **1,000 employees** at Cruise lost their jobs due to the layoffs. This included important leaders like the **CEO** and the **chief safety officer**.
How does GM’s Super Cruise technology work?
**Super Cruise** allows cars to drive themselves on certain roads. It uses **cameras** and **GPS** to help the car stay in its lane and follow traffic rules.
What are the dangers of robotaxis mentioned in the news?
One danger of robotaxis is that they can cause accidents. For example, a Cruise robotaxi injured a **pedestrian** by dragging them. This raises concerns about their safety on public roads.
What changes is GM making to its self-driving car plans?
GM is shifting its focus from robotaxis to improving self-driving features for personal cars like the **Super Cruise** system, which they believe can make more money.
Why did people in San Francisco feel relieved about the robotaxi shutdown?
People in San Francisco felt relieved because the robotaxis caused problems like **traffic jams**. With the shutdown, they won’t have to worry about these self-driving cars blocking the streets.
Summary
The content discusses General Motors’ significant shift away from its robotaxi venture, Cruise, by announcing layoffs of approximately 1,000 employees, including key executives. This decision follows GM’s full acquisition of Cruise and a strategic pivot toward enhancing its Super Cruise technology for personal vehicles, which is expected to generate substantial revenue. The company has faced challenges with Cruise, including serious incidents and financial losses from its robotaxi operations. As GM refocuses its efforts, the decision to exit the robotaxi market alleviates concerns for residents in cities like San Francisco, where autonomous vehicle incidents have raised public safety issues.